Tips for Healthy Eating, Diabetes Prevention and Management
Diabetes occurs when your body cannot properly use and store food for energy. Your body’s main source of energy is called glucose, a form of sugar that comes from foods that contain carbohydrate, such as fruit, milk, some vegetables, grains, starch foods and sugar. When your body cannot use glucose for energy, the glucose builds up in your blood leading to high blood sugar levels.
Depending on the type of diabetes, pills, insulin, or other injectable medication may be needed to manage blood sugar.
| Type of Diabetes | How this type is treated |
|---|---|
| Type 1 diabetes The pancreas does not produce insulin. Glucose builds up in your blood instead of being used for energy. |
|
| Type 2 diabetes The pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or your body does not properly use the insulin it makes. |
|
| Pre-diabetes Blood glucose levels that are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. |
|
| Gestational diabetes High blood sugar that happens during pregnancy. |
|
Eat a variety of healthy foods each day

Even if someone is taking diabetes medications, all types of diabetes are managed better with healthy eating. Knowing what to eat and how much to eat will help you manage your blood sugar levels. Eat more vegetables. These are very high in nutrients and low in calories.Include lean animal proteins such as fish, chicken, lean meats, low-fat cheese, eggs, dried beans and peas as part of your meal. Select plant oils such as olive and canola, and nuts instead of animal fats and coconut oil. Have yogurt and a piece of fruit to complete your meal. Eat small portions of grains and starches including rice, potato, pasta, cereals, breads, corn.
Handy portion guide
Your hands can be very useful in estimating the right amount of food to eat. When you are planning a meal, use the following portion sizes as a guide:
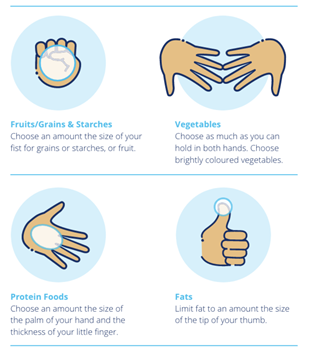
Fruits/Grains & Starches
Examples: Orange, apple, potatoes, brown rice, spaghetti
Vegetables
Examples: Broccoli, lettuce, green beans, bell peppers
Protein Foods
Examples: Lean beef, chicken, pork, fish, eggs, tofu, yogurt, milk (skim, 1%), cheese
Fats
Examples: Non-hydrogenated margarine, canola oil, olive oil, peanut oil
Being well helps you and your family
Here are some tips to help you before you see a registered dietitian.
| When to eat? | |
| Tips | Why? Because… |
|
It provides a good start to the day. Eating the right amount at the right time helps keeps your blood glucose in balance. |
|
Pack healthy foods with you (such as whole grain crackers, cheese and vegetables) in case you are going to be away from home at meal time. |
This helps you have healthy choices, wherever you go. |
| What to Eat | |
| Eat a variety of foods at each meal or snack | Choosing foods from all food groups will make sure that the bodhy gets all the nutrients it needs to be healthy. |
|
Limit sugars and sweets such as regular soft drinks, desserts such as donuts, ice cream, cakes, candies, jam and honey. Artificial sweeteners can be safe in small amounts. |
The more sugar you eat or drink, the higher your blood glucose will be. |
|
Limit high fat and greasy foods, such as fries, potato chips and cookies. Prepare foods in a healthy way, such as baking, broiling, braising, steaming, poaching, roasting, stir-frying, sautéing. |
High fat foods are hard on the heart and may cause weight gain. A healthy weight is easier for the heart and helps with blood glucose control. |
|
Eat at least two different kinds of vegetables at each meal. |
Vegetables are high in the nutrients the body needs to be healthy. |
|
Include foods high in fibre (whole grain breads, cereals, sweet potato, lentils, dried beans, brown rice, vegetables and fruits). |
High fibre foods help you feel full, and lower your blood glucose and cholesterol levels. |
|
If you are thirsty, drink water. |
Drinking regular pop, fruit juice, sweetened coffee and tea, will raise your blood glucose. |
| How much to eat | |
|
Eat slowly and stop when you feel full and satisfied. |
The right amount of food gives your body what it needs to be healthy. If you eat too much, your body will store the extra energy as fat. You may also gain weight by eating more than you need. |
Limit alcohol consumption
Alcohol can affect blood glucose levels. It can also cause you to gain weight and change how your body uses medicine. Talk to your healthcare team about how much alcohol is safe for you.
Take care of your whole body for a healthier life! Manage your diabetes in a healthy way!
Related Content

Diabetes-friendly recipes
Try our delicious recipes for every dietary need and any meal of the day—including snacks.
Browse recipes About Diabetes-friendly recipes

Tools & resources
We've got dozens of tools and resources to help you understand and manage diabetes.
Tools & resources About Tools & resources